What exactly is a
Eosinophilic esophagitis?
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, inflammatory disease of the esophagus characterized by an excessive accumulation of eosinophilic white blood cells in the esophageal mucosa. This causes thickening and narrowing of the esophagus, which can cause symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, retrosternal pain, heartburn, vomiting and food blockage.
Although the exact cause of EoE is not yet fully understood, it is increasingly being diagnosed, which has sparked interest in intensive research and better treatment options.
About the symptoms
More information
Important facts about eosinophilic esophagitis
Symptoms and consequences of eosinophilic esophagitis:
- Difficulty swallowing
- Pain behind the breastbone (retrosternal pain)
- Abdominal pain
- Heartburn
- Vomiting
- Food Blocks
- Thickening and narrowing of the esophagus
- Long-term complications such as scarring and additional narrowing of the esophagus (strictures)
Symptomatology in childhood and adulthood:
In children and adolescents, difficulty swallowing, abdominal pain, and vomiting are often the primary symptoms. In addition, children may experience growth problems, often accompanied by food refusal.
Adults are more likely to suffer from heartburn and retrosternal pain. Nevertheless, some symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing, may be similar in both age groups. Accurate diagnosis by endoscopic examination and biopsy is important regardless of age to ensure the best possible treatment.
What is the role of eosinophilic cells in the development of EoE?
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is named for the specific inflammatory cells involved in the disease: eosinophilic granulocytes. This unique type of white blood cell (leukocyte) plays a critical role in immune defense against parasites and allergic reactions.
At the same time, the word "esophagitis" is the medical term for inflammation of the esophagus (food pipe). In EoE, for reasons as yet unknown, excessive numbers of these eosinophilic cells accumulate in the mucosa of the esophagus, causing the characteristic inflammation.
What are the causes of eosinophilic esophagitis?
The exact causes of EoE are not fully understood, but it is thought that both genetic and environmental factors may play a role. Particularly relevant environmental factors, in addition to airborne allergens, are certain food allergens, which is why the disease is also considered a special form of food allergy. It is also more common in people who already have atopic dermatitis, asthma or other allergies.
The following allergens can cause excessive accumulation of eosinophils in the esophagus in affected individuals:
Food with animal milk
Grains containing gluten, especially wheat
Less frequently also eggs, nuts, soy and seafood
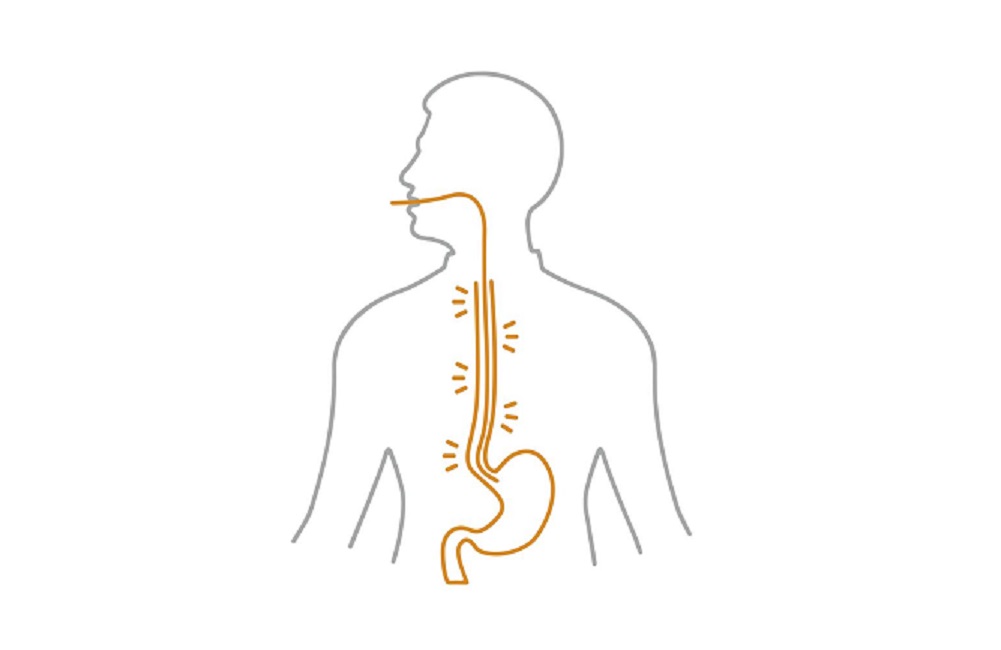
How is eosinophilic esophagitis diagnosed?
Because symptoms can be confused with other gastrointestinal disorders, accurate diagnosis is critical. This is usually carried out using a combination of clinical examinations and endoscopic procedures. Here are the main steps of the diagnosis:
Medical history and clinical examination
Medical history and clinical examination
Taking the detailed medical history and symptoms
Endoscopy
Endoscopy
Insertion of a flexible tube (endoscope) with a camera and a light source through the mouth into the esophagus
Biopsy
Biopsy
Taking small tissue samples (biopsies) from the mucosa of the esophagus
Microscopic examination
Microscopic examination
Laboratory examination of tissue samples taken under the microscope to detect an elevated number of eosinophil cells
Exclusion of other causes
Exclusion of other causes
Causes of similar symptoms such as gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) or eosinophilic gastroenteritis.
What to do in case of eosinophilic esophagitis?
Change of diet
A low-allergen diet can help identify and avoid potential triggers of EoE. Together with a specialist, such as a nutritionist:in or allergist:in, certain foods that may exacerbate symptoms can be identified and these should be removed from the diet.
Careful eating behavior
Slow and thorough chewing of food can reduce the strain on the esophagus and facilitate digestion. Eat in a relaxed environment, without distractions or hurry. Instead of large meals, several smaller portions can be eaten throughout the day to reduce stress on the esophagus. Also, avoid lying down immediately after eating. An upright position can help reduce reflux of stomach acid.
Drug treatment and dilatation
In some cases, the doctor:in may prescribe anti-inflammatory medications to reduce inflammation in the esophagus. In addition, endoscopic dilation (widening) of the esophagus may be considered to relieve narrowing. These treatment measures should be carried out under the careful supervision of a medical specialist in order to minimize possible risks.
Sources
Please note that all content provided regarding individual medical conditions, treatments, procedures, etc. is general information and may vary depending on the physician:in and individual case and initial situation.
For more detailed information, please always consult your doctor.
Biedermann, L. et al: Food-induced immediate response of the esophagus-A newly identified syndrome in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis, in Allergy 2021, 76(1):339-347; doi: 10.1111/all.14495
Herold, G. (Ed.): Internal Medicine, self-published, 2022