What is a
Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU)?
Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) is a type of chronic skin disease characterized by the appearance of recurrent itchy wheals (urticaria) on the skin. “Chronic” means that the symptoms persist over a period of at least six weeks or longer.
CSU occurs spontaneously and without a recognizable cause, which means that it is not due to a specific allergy or infection. The cause of CSU is not always known, but it is thought that a faulty immune response of the body may play a role.
About the symptoms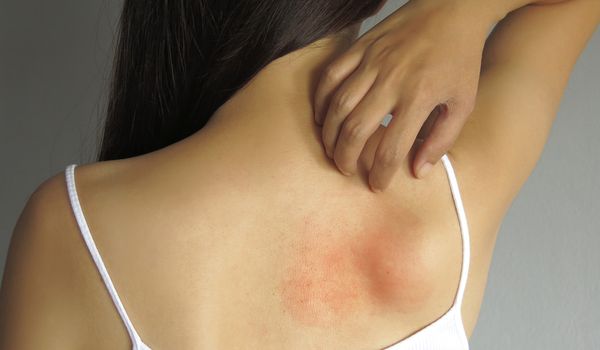
More information
Important facts about chronic spontaneous urticaria
Symptoms and consequences of chronic spontaneous urticaria:
- Appearance of itchy, raised skin rashes (wheals or nettles)
- The rashes vary in size and shape
- Wheals can move quickly and appear on different parts of the body
- The rashes can last from minutes to hours
- Symptoms can be unpredictable and occur without a recognizable trigger
- Accompanying symptoms such as itching, burning or pain are possible
- In some cases, swelling (angioedema) of the deeper layers of the skin may occur, particularly around the eyes, lips or genitals
- The symptoms can have a significant impact on quality of life, particularly due to the itching and recurring nature of the condition
Which foDifferent forms of urticaria
There are various forms of urticaria, which are differentiated according to the trigger and symptoms. Here are some other forms of urticaria:
- Chronic spontaneous urticaria: Without a real trigger, this form is the most common.
- Cold urticaria: Triggered by cold, leads to itchy skin rashes after exposure to cold.
- Pressure urticaria: Reaction to pressure or friction of the skin, e.g. from tight clothing, leads to skin rashes.
- Dermographism: Appearance of redness and swelling of the skin in response to light pressure or scratching of the skin.
Causes of chronic spontaneous urticaria
The exact causes of chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) are not yet fully understood, but it is thought that a faulty immune response of the body may play a role. In CSU, the immune system reacts to unknown stimuli and triggers an inflammatory reaction that leads to the characteristic skin symptoms.
It is important to note that in many cases the cause of the CSU remains unknown. In these cases, treatment may be aimed at relieving the symptoms rather than eliminating the underlying cause.
Autoimmune diseases
Autoimmune diseases
In some patients with CSU, antibodies directed against the body's own structures are detectable in the blood, indicating that autoimmune diseases may play a role.
Infections
Infections
Viral infections, especially hepatitis B or C, can sometimes trigger or worsen CSU.
Hormonal changes
Hormonal changes
Some women develop CSU during pregnancy or after the menopause, which points to hormonal changes as a possible cause.
Stress and emotional strain
Stress and emotional strain
Stress can affect the body in various ways and compromise the immune system, potentially triggering or exacerbating CSU symptoms.
Food and medication
Food and medication
Although CSU is not caused by food allergies or drug intolerances, certain foods and medications (e.g. aspirin, certain painkillers or blood pressure medication) can exacerbate the symptoms of CSU.
How is chronic spontaneous urticaria diagnosed?
The diagnosis of chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) requires a thorough examination by medical professionals. Here are the steps that are usually taken when diagnosing CSU:
Medical history and physical examination
Exclusion of other causes and forms of urticaria
Diagnostic criteria according to the guideline on the length and intensity of nettles

What to do with chronic spontaneous urticaria
The treatment of chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) aims to alleviate the symptoms, reduce the frequency of skin rashes and improve the quality of life.
It is crucial that you see a doctor if you suspect CSU. Each case is unique, and an individualized treatment strategy is developed based on your specific symptoms and needs.
Trigger avoidance
Although CSU often has no specific triggers, it can still be helpful to avoid factors that could exacerbate symptoms, such as extreme temperatures, stress or certain foods.
Lifestyle and stress
Stress management techniques, sufficient sleep and a healthy diet can help to improve symptoms.
Treatment with medication
To date, there is no treatment that can permanently cure chronic urticaria. In many cases, however, it is possible to identify the causes or triggers of hives. With the help of modern medication, there is also hope of achieving freedom from symptoms. If chronic spontaneous urticaria is diagnosed by a doctor and the medical history provides no evidence of a trigger, treatment of the symptoms (itchy wheals and/or swelling) should at least be started as soon as possible.
Sources
Please note that all content provided regarding individual medical conditions, treatments, procedures, etc. is general information and may vary depending on the physician:in and individual case and initial situation.
For more detailed information, please always consult your doctor.
Deutsches Arztebl 2022; 119(9): [6]; DOI: 10.3238/PersOnko.2022.03.04.01; Staubach-Renz, Petra; Metz, Martin
Maurer M, Weller K, Bindslev-Jensen C, et al. Unmet clinical needs in chronic spontaneous urticaria: A GA(2)LEN task force report. Allergy 2011;66:317-330.
Website of the ECARF - European Centre for Allergy Research Foundation. (accessed on 09.07.2021)
Link