What exactly is a
Birch pollen allergy?
Birch is one of the strongest and most aggressive allergens among tree pollen. In Europe, most pollen allergy sufferers react to birch pollen, not least because of the extremely high number of allergens: A single tree can release up to 100 million pollen! Every two years there is a mast year in which a particularly large amount of pollen is released. Birch pollen allergy sufferers often also have reactions to pollen from related tree species and can suffer from cross-reactions to certain foods.
About the symptoms
More information
Important facts about birch pollen allergy
Symptoms and consequences of birch pollen allergy:
- Sneeze
- Runny nose
- Itchy eyes
- Redness and swelling of the eyes
- Breathing difficulties
- Tightness in the chest
- Tiredness and exhaustion
- Impairment of sleep quality
When is birch pollen season?
The birch pollen season usually takes place in spring, normally between March and June. People who suffer from a birch pollen allergy typically experience increased symptoms during this time. The exact duration and intensity of allergy symptoms can vary depending on individual sensitivity, geographical location and weather conditions. It is advisable to check the pollen calendar and local forecasts to find out when the birch pollen count is highest in your area.
What are the causes of a birch pollen allergy?
The cause of birch pollen allergy is a hypersensitive reaction of the immune system to the proteins in the pollen of birch trees. When a person with such an allergy comes into contact with pollen, the immune system recognizes it as a threat and triggers defence mechanisms. It produces antibodies, in particular immunoglobulin E (IgE), to fight the supposed threat. Further contact with the pollen then results in the release of inflammatory substances such as histamine, which leads to the typical allergic symptoms. The exact reasons for the development of a birch pollen allergy are not yet fully understood, but both genetic and environmental factors play a role.
How is a birch pollen allergy diagnosed?
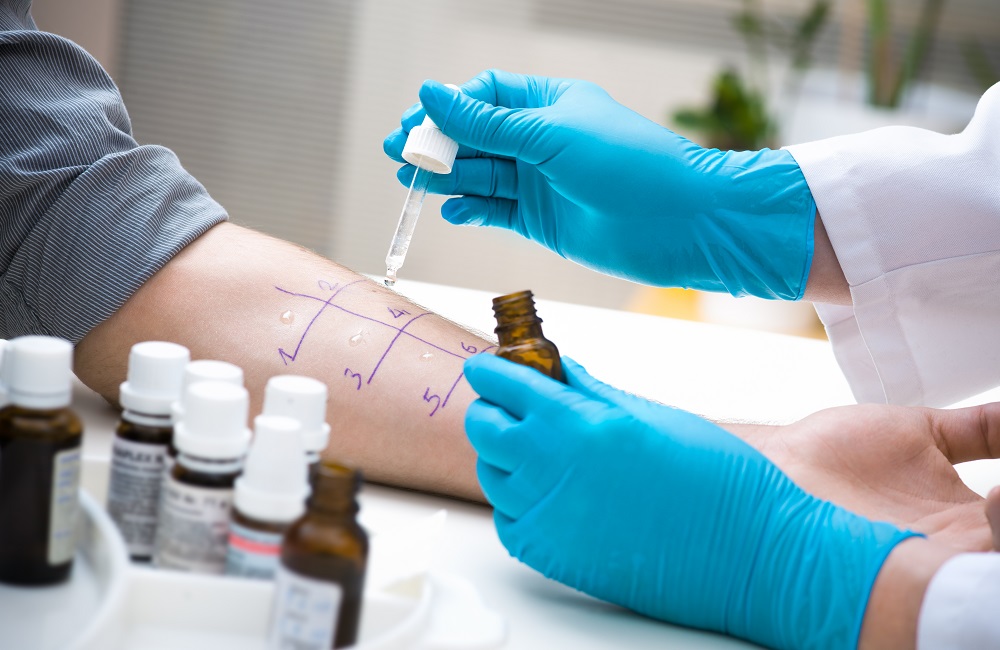
A birch pollen allergy is usually diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination and specific allergology tests. At the beginning, the doctor will ask the patient about their symptoms and the temporal connection with contact with birch pollen. A physical examination can then be carried out to rule out other possible causes. The most important diagnostic test for a birch pollen allergy is the allergy test, in which various methods such as the skin prick test or the blood test (specific IgE antibodies) are used. These tests show whether there is an allergic reaction to birch pollen and how severe the reaction is. In some cases, a provocation test may be necessary to confirm or rule out the allergy. An allergy specialist can interpret the results and make an accurate diagnosis.
Allergy skin test (prick test)
Blood test (specific IgE antibodies)
Provocation test
What to do if you are allergic to birch pollen?
Avoid plants and trees if you are allergic to birch pollen
In the case of birch pollen allergy, cross-reactions can occur in which the immune system shows similar reactions to other allergenic substances. This is because the main allergen of birch Bet v1 has many counterparts. Plants such as alder, hornbeam, oak, chestnut and beech should therefore be avoided. The following foods can also have a negative effect on the allergy. Apples, pears, stone fruit (cherries, peaches, plums, etc.), nuts (especially hazelnuts), celery, carrots, potatoes, soybeans, peanuts, spices (such as aniseed, peppermint)
Dealing with a birch pollen allergy in everyday life
Avoid spending long periods outdoors and keep windows and doors closed as much as possible to reduce the amount of pollen entering your home. If possible, only ventilate your home at times when there is little birch pollen, preferably after dark. Also install special pollen screens on windows and doors and use air purifiers in your rooms and a vacuum cleaner with a suitable filter. Wash your hair before going to bed. It is also helpful to dry the laundry in a tumble dryer or indoors to prevent pollen from settling in it.
Medical treatment of birch pollen allergy
Contact your family doctor, dermatologist or allergist. Treatment with antihistamines is often sufficient for mild symptoms. These can be administered in the form of tablets, nasal spray or eye drops. However, if the symptoms are very severe, hyposensitization is often recommended. With this form of therapy, the body gradually becomes accustomed to the allergy-causing substances. New treatment options are also being developed in clinical trials. More information (link to the clinical studies page)
Sources
Bitte beachte, dass sämtliche zur Verfügung gestellten Inhalte zu den einzelnen Krankheitsbildern, Behandlungen, Abläufen etc. generelle Informationen sind und je nach Ärzt:in und individuellem Fall und Ausgangslage variieren können.
Für genauere Auskünfte konsultieren Sie bitte immer Ihre:n Ärzt:in.
Hay fever in adolescents and adults, NCBI
LinkHay fever: Overview, NCBI
LinkHaftenberger M, Laußmann D, Ellert U, et al. Prevalence of sensitization to inhalant and food allergens. Bundesgesundheitsblatt - Health Research - Health Protection. 2013;56(5):687-697. DOI:10.1007/s00103-012-1658-1
Biedermann T, Winther L, Till SJ, Panzner P, Knulst A, Valovirta E. Birch pollen allergy in Europe. Allergy. 2019;74(7):1237-1248. DOI:10.1111/all.13758
Birch pollen allergy: Triggers, symptoms & treatment (allergiecheck.de)
Link