What is actually a
Skin fungus?
A skin fungus, also known as dermatophytosis or tinea, is a common fungal infection of the skin caused by various types of fungi. The most common pathogens are dermatophytes, which include Trichophyton, Microsporum and Epidermophyton. These fungi feed on keratin, a protein found in skin, hair and nails. These can infect the outer layer of the skin.
Fungal skin infections can cause unpleasant symptoms and spread to other parts of the body or people. Transmission occurs through direct contact with infected areas of skin or through indirect contact via contaminated objects such as towels, clothing or floors.
About the symptoms
More information
Important facts about skin fungus
Symptoms and consequences of a skin fungus
The symptoms of a fungal skin infection vary depending on the part of the body affected and the type of fungus, but may include the following signs:
- Red, scaly patches on the skin.
- Itching and skin irritation
- Formation of blisters or pustules.
- Cracks or flaking
- Hair loss (in cases of scalp fungus).
- Thickening and discoloration of the nails (nail fungus)
What forms of skin fungus are there?
The most common forms of skin fungus are: Tinea corporis (ringworm): This form occurs on the smooth skin of the body and causes round, red, scaly patches that spread outward and often heal in the center, making them appear ring-shaped. Tinea pedis (athlete's foot): Athlete's foot is an infection of the skin between the toes and on the soles of the feet. It can lead to redness, scaling, itching, burning and blistering. Tinea cruris (jock itch): This form affects the groin area and is often seen in men. It causes redness, itching and possibly painful rashes in the groin folds. Tinea capitis (scalp fungus): This infection affects the scalp and leads to hair loss, scaly skin and sometimes inflamed lesions. Tinea barbae (beard fungus): Beard fungus occurs in the beard area and on the face and can cause redness, dandruff and hair loss. Tinea manuum (hand fungus): This form affects the hands and can lead to redness, scaling and itching. Tinea unguium (nail fungus): Nail fungus affects the nails of the fingers and toes and leads to thickening, discoloration and fragility of the nails.
What causes skin fungus?
The causes of fungal skin infections are usually fungi known as dermatophytes. These fungi thrive in moist and warm environments and can live on the skin without causing immediate symptoms. However, if certain conditions are met, they can multiply and cause an infection. The following causes can be the trigger for skin fungus.
Contact with infected persons or animals
Contact with infected persons or animals
Fungal skin infections are highly contagious and can easily be transmitted from one infected person or animal to another.
Contact with contaminated surfaces
Contact with contaminated surfaces
Fungal spores can survive on surfaces such as carpets, towels, clothing, bedding and floors. If a person comes into contact with such a contaminated surface, the fungal spores can be transferred to the skin and cause an infection.
Moisture and sweat
Moisture and sweat
Fungi thrive in humid environments. Sweating and wearing tight, damp clothing or shoes encourage the growth of fungi and increase the risk of infection.
Weakened immune system
Weakened immune system
People with a weakened immune system, whether due to certain illnesses, medication or other factors, are more susceptible to fungal skin infections.
Community facilities
Community facilities
Places such as changing rooms, swimming pools, showers and gyms provide an ideal environment for the spread of fungal skin infections as they are damp and warm and many people share these facilities.
How is skin fungus diagnosed?
An experienced doctor, usually a dermatologist or a general practitioner, can diagnose a skin fungus.
Medical history
Physical examinations
Wood light test with ultraviolet light
Swab or skin sample
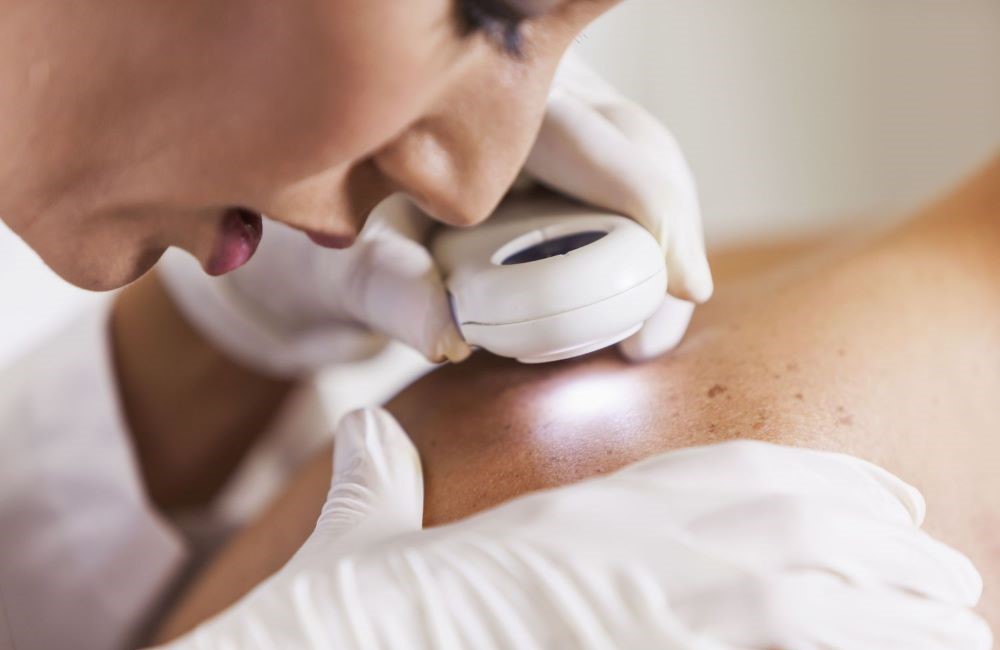
What to do with fungal skin infections?
Measures for fungal skin infections
Fungal skin infections are usually treated with antimycotics, which can be administered topically (applied to the skin) or orally (in the form of tablets). It is important to adhere to the entire prescribed treatment period to ensure that the fungus is completely eliminated and recurrence is prevented.
Hygiene
To avoid fungal skin infections, it is advisable to maintain good hygiene, not to share personal items such as towels or razors and to avoid walking barefoot in public areas such as swimming pools or changing rooms.
Sources
Please note that all content provided regarding individual medical conditions, treatments, procedures, etc. is general information and may vary depending on the physician:in and individual case and initial situation.
For more detailed information, please always consult your doctor.
MSD Manual, By Denise M. Aaron , MD, Dartmouth Geisel School of Medicine, Sep 2021
Fungal infections of the skin, Andrea Lubliner, Brit Weirich (medical author, M.A. Multilingual Communication), Last update: 06.01.2022
S1 guideline onychomycosis 12/05/2022
Guidelines of the German Dermatological Society and the German-speaking Mycological Society, Tinea of the free skin, 10/2008